
USB ports are essential interfaces that connect a variety of devices to your computer, allowing for data transfer and power supply.
They’re designed to enhance connectivity, found in both wired and wireless forms.
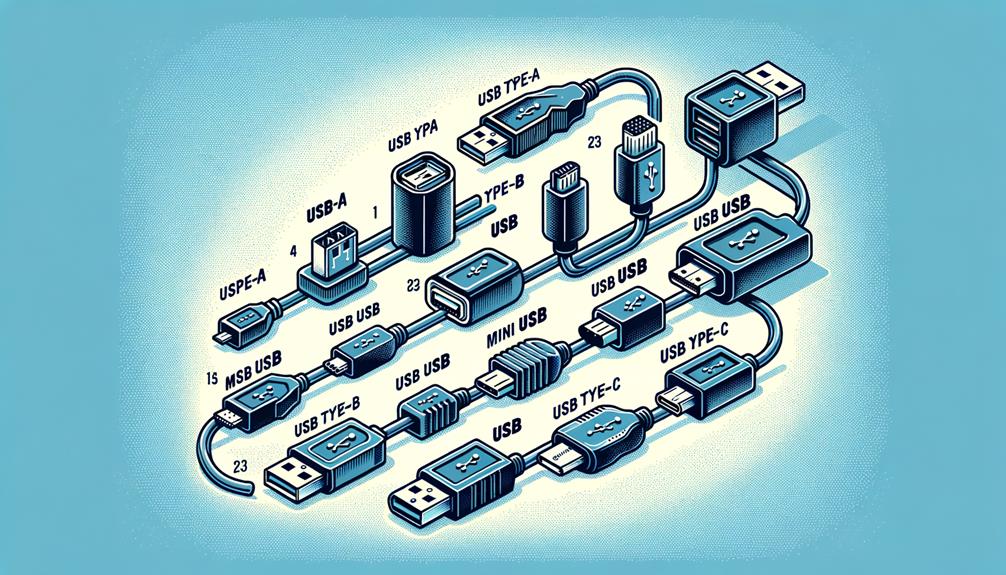
Common types include USB-A, which is rectangular, and USB-C, known for its reversible design and fast data and power delivery. Other variants like Mini-USB and Micro-USB cater to specific devices.
USB standards have progressed through several versions, with USB4 being the latest, offering high data speeds and integrating Thunderbolt 3 protocols.
Troubleshooting USB issues may involve checking for physical damage or updating drivers.
Explore further to discover more possibilities with USB ports.
Quick Summary
- USB ports are interfaces for connecting devices to computers, supporting both data transfer and power supply.
- Various USB connector types include USB-A, USB-C, Mini-USB, and Micro-USB, each serving different connectivity roles.
- USB standards have evolved from USB 1.0 to USB4, enhancing speed and power delivery capabilities.
- Common USB issues involve checking for physical damage, updating drivers, and testing on different hardware.
- Alternatives to USB ports include Thunderbolt for high-speed data transfer, HDMI, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct, and NFC for diverse connectivity options.
Defining USB Ports
USB ports, standing for Universal Serial Bus, are standard interfaces for connecting a wide range of devices and peripherals to computers and other electronic devices, enabling both data transfer and power supply.
The broad USB port compatibility across various devices enhances user experience by simplifying connectivity and reducing the need for multiple adapters.
You’ll find these ports in both wired and wireless forms, accommodating a diverse array of gadgets from smartphones to external hard drives.
One of the primary benefits of USB ports is their ability to transmit data and power simultaneously, streamlining operations and eliminating excess cables.
This dual functionality not only guarantees efficiency but also supports the quick charging of devices, making USB ports indispensable in the digital age.
Types of USB Connectors
Several types of USB connectors exist, each designed for specific devices and purposes, including USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, Mini-USB, and Micro-USB.
You’ll find each has a unique shape and size, tailored for distinct roles in connectivity.
Here’s how you can visualise and manage them:
- USB-A: Most common, rectangular interface; ideal for host devices like computers.
- USB-C: Reversible and versatile, supports faster data and power delivery, enhancing compatibility across different devices.
- Mini-USB and Micro-USB: Smaller, primarily for older smartphones and certain cameras.
Understanding the compatibility comparison between these types will streamline your cable management techniques, ensuring you use the right connector for the right device, thereby avoiding unnecessary clutter and optimising your setup’s efficiency.
Evolution of USB Standards
As technology has advanced, the standards for USB have also evolved, progressing from USB 1.0 to the much faster and more versatile USB4.
You’ve witnessed a remarkable leap in USB data speeds and power delivery capabilities.
USB4 isn’t just about speed; it integrates Thunderbolt 3 protocols, pushing data transfer rates to unprecedented levels and expanding connectivity options.
Additionally, USB-PD (Power Delivery) technology has become a standard for charging devices, providing a fast and efficient power supply.
Importantly, USB4 mandates the use of the Type-C connector, ensuring seamless compatibility across the latest devices.
Troubleshooting USB Issues
Occasionally, you may encounter issues with your USB connections; here’s how to effectively troubleshoot these problems.
The challenges often pertain to USB power supply and USB data transfer, and addressing them can restore functionality efficiently.
- Inspect Physical Condition:
Check for any physical damage on the USB port or cable. Bent or broken pins can impede both power supply and data transfer, leading to connectivity failures.
- Update USB Drivers:
Make sure that your device’s USB drivers are current. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues that disrupt proper functioning.
- Test on Different Hardware:
Try using the USB device with another computer. This step helps determine if the issue is with the USB device itself or specific to your computer’s USB port.
USB Port Alternatives

While USB ports are commonly used, alternatives like Thunderbolt and HDMI cables offer specialised capabilities for different data transfer needs.
Thunderbolt vs. USB C is a significant comparison; Thunderbolt provides higher data transfer rates and daisy-chaining of devices, unlike USB C.
Additionally, you’ve got wireless technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Direct as viable options, eliminating the clutter of wires.
| Technology | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Thunderbolt | High-speed data transfer |
| HDMI | Audio-visual transmission |
| Bluetooth | Short-range connectivity |
| Wi-Fi Direct | Peer-to-peer connections |
| NFC | Contactless communication |
These alternatives provide you with flexibility depending on your specific requirements, whether you’re aiming for faster data speeds or convenient wireless setups.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are There 2 Types of USB Ports?
Yes, there are two primary types. You’ll find variations in port durability and speed, with Type-A offering standard compatibility and Type-C featuring enhanced transfer rates and reversible design for modern device interfaces.
What Does a USB Look Like?
You’ll notice USBs typically have a rectangular shape, featuring colour variations and a distinct connector design with a central plastic tab for alignment. Look for the trident-like symbol indicating USB compatibility.
How Do I Know if My USB Is A or C?
To determine whether your USB is Type A or C, examine its shape. Type A is rectangular, while Type C is oval and reversible. Consider connection speed and compatibility issues with your devices.
What Is the Difference Between a USB Port and a Charging Port?
A USB port supports data transfer and device connection, while a charging port primarily focuses on power delivery, lacking the broader port functionality of its counterpart.
Conclusion
So, you’ve navigated the complex world of USB ports. From understanding the various connectors—Type-A, Type-C, Micro-USB—to grasping the evolution from USB 1.1 to USB4, you’re now equipped to handle any USB issues that come your way.
If USB doesn’t meet your needs, consider alternatives like Thunderbolt or HDMI. Remember, the right connection can make all the difference in maximising your device’s performance.
Keep this guide handy as you continue to connect and power your digital world.
